Onde Q
sans rapport avec une onde Q de nécrose.
Il s’agit d’ondes Q non physiologiques, élargies et/ou amples, observées au cours :
- de certaines formes d’hypertrophie ventriculaire avec amplification de l’onde q septale (Cf. Cardiomyopathie hypertrophique, cœur pulmonaire chronique…). Dans ce cas, l’onde R qui succède est souvent ample, à l’opposé de ce qu’on observe dans une séquelle d’infarctus [1].
- de certaines formes de cardiomyopathie hypertrophique ou d’hypertrophie septale (responsable d’ondes Q en territoire inférieur) (voir synthèse Madias 2024 [2]). L’onde R reste présente après l’onde Q et la repolarisation peut être normale ou d’allure ischémique.

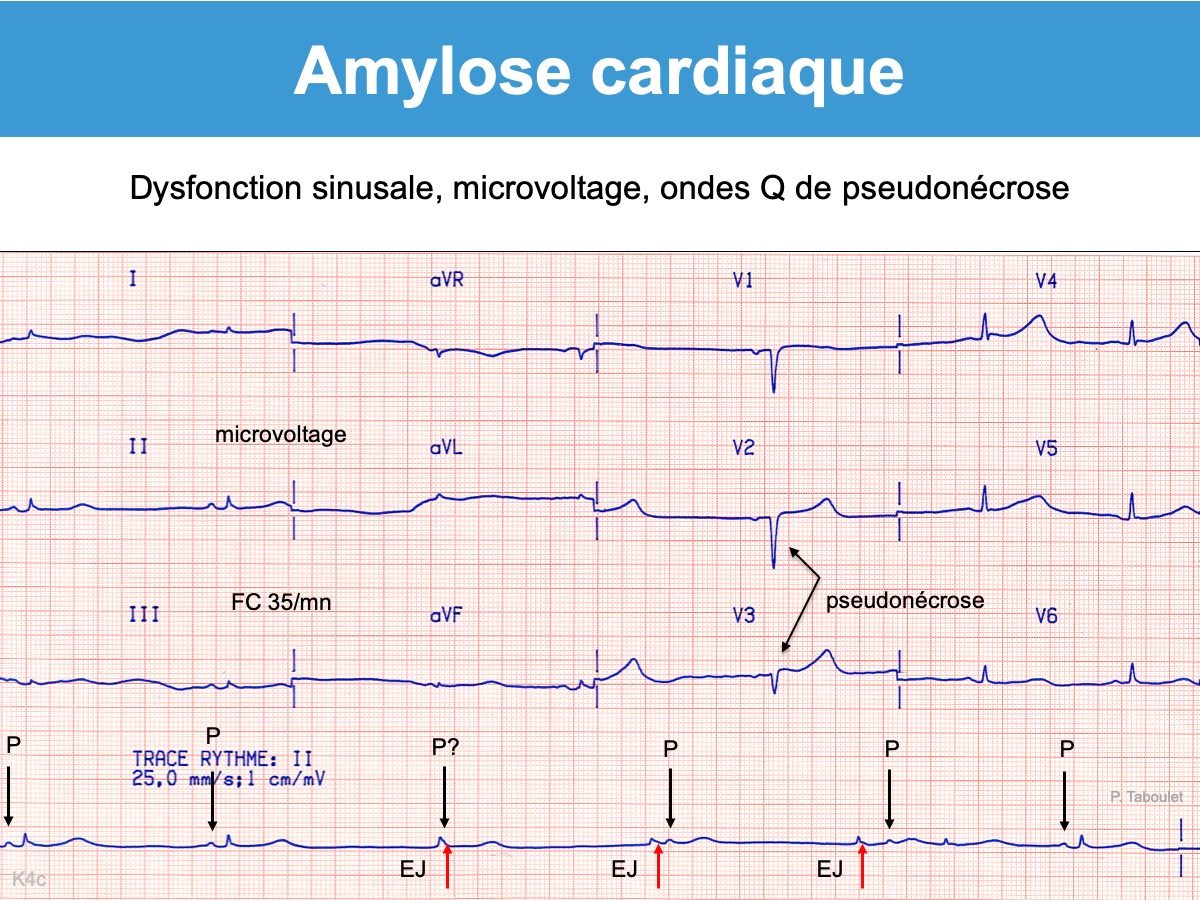
- de certaines formes d‘atrophie et fibrose du muscle ventriculaire (Cardiopathies restrictives telles une amylose cardiaque, maladie de Fabry, hémochromatose, sclérodermie systémique, fibrose enodomyocardique tropicale, lymphome diffus…). Dans ce cas, le tracé est souvent microvolté et les QRS remplacés par des ondes QS.
Fibrose cardiaque (en français) :https://www.academie-medecine.fr/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/775-784.pdf
[1] Robert T. Short, Bei Hu, Laszlo Littmann. A malignant electrocardiogram. Circulation 2020;142:1989-92.
L’aspect peut être confondu avec un infarctus ST+ évolutif ( » pseudo infarction ECG « ) [1] (Cf. Sus-décalage de ST. Etiologies non ischémiques). In summary, our patient initially presented acutely with symptoms and ECG findings concerning for ST-segment–elevation myocardial infarction. She was found to have cardiac malignancy and nonobstructive coronary artery disease. The predominant apical location of her primary cardiac lymphoma resulted in a sustained pseudoinfarction pattern in the ECG.
[2] Madias JE. The syndrome of inferior non-infarctional Q-waves due to segmental basal left ventricular hypertrophy. J Electrocardiol. 2024 Aug 22;86:153785.