Vidéo formation l’ECG toxique. YouTube P. Taboulet (25 min)
Ce module fait la synthèse des signes les plus évocateurs d’un ECG « toxique », c’est à dire d’un ECG modifié par des toxiques cardiotropes qui agissent sur le système sympathique et parasympathique ou sur le potentiel d’action des myocytes.
L’exemple type d’ECG toxique résulte de l’action des substances « stabilisant de membrane » ou « quinidine like » qui bloque essentiellement les canaux sodiques et potassiques de dépolarisation et repolarisation rapide des myocytes ventriculaires (Voir antidépresseurs cycliques, neuroleptique, cocaïne, chloroquine, bêtabloquant).
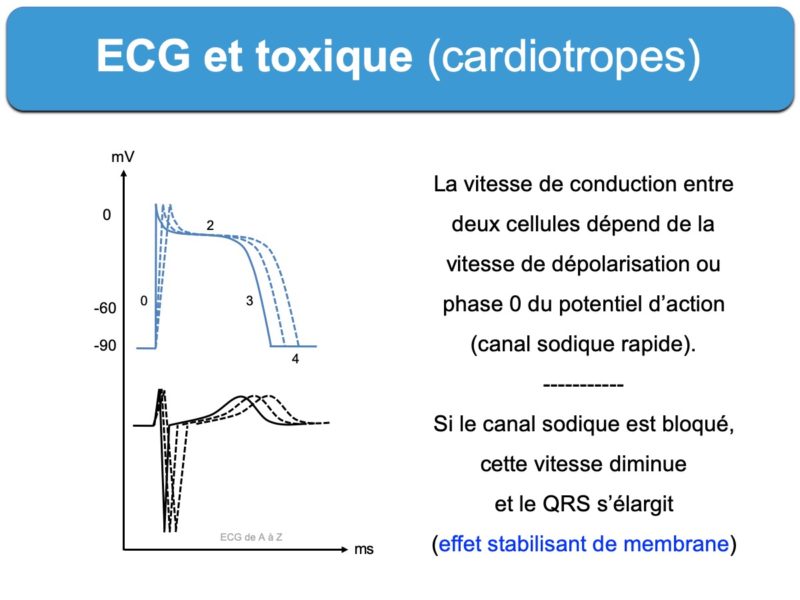
Nous verrons certains exemples pathognomoniques dont certains tracés d’intoxication digitaliques bétabloquant, flécaïnide, cocaïne et autres toxiques auxquels on ne pense pas toujours.
Dix signes sont à connaître…. Plus il y a de signes, plus il y a (mal)chance qu’un patient soit intoxiqué par des cardiotropes. Certains signes sont simples à rechercher et particulièrement évocateurs… Voir ci-dessous.
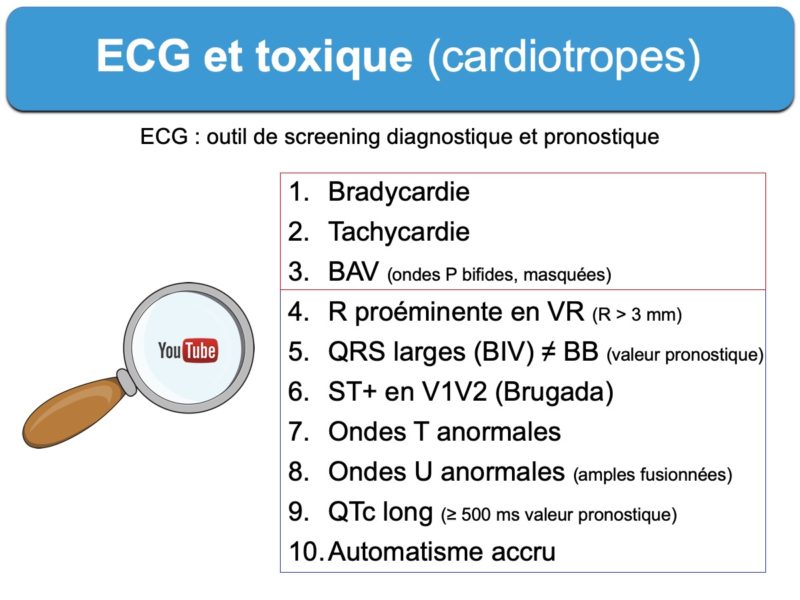
Une riche iconographie et bibliographie illustre la vidéo.
Niveau : Médecin urgence, cardiologue, réanimation
——————
Voir aussi
- Intox cardiotropes cours DESCMU 2017 : Dr Gainnier (Timone) : cours très complet (téléchargeable)
- Nombreux ex d’ECG toxiques sur Google
- Lire aussi ce beau cas clinique au sujet du loperamide
- Playlist YouTube : L’ECG métabolique
TRAITEMENT
Lavonas EJ, Akpunonu PD, Arens AM, Bet al; American Heart Association. 2023 American Heart Association Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Cardiac Arrest or Life-Threatening Toxicity Due to Poisoning: An Update to the American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2023 Oct 17;148(16):e149-e184. (téléchargeable)
TOP 10 TAKE-HOME MESSAGES FOR MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH CARDIAC ARREST OR LIFE-THREATENING TOXICITY DUE TO POISONING
-
Treatment of cardiac arrest and life-threatening toxicity due to poisoning often requires specialized treatments that most clinicians do not use frequently such as antidotes and venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, in addition to effective basic and advanced life support. Timely consultation with a medical toxicologist, clinical toxicologist, or regional poison center facilitates rapid and effective therapy.
-
Opioid overdose remains the leading cause of cardiac arrest due to poisoning in North America. Naloxone administration may reverse respiratory arrest, preventing progression to cardiac arrest.
-
High-dose insulin therapy is recommended early in the treatment of patients with life- threatening β-blocker and calcium channel blocker poisoning.
-
Standard advanced life support with the addition of administration of sodium bicarbonate is appropriate for the treatment of life-threatening dysrhythmias caused by cocaine or other sodium channel blockers.
-
If cyanide poisoning is suspected, do not wait for confirmatory testing. Treat immediately with hydroxocobalamin (preferred) or sodium nitrite plus sodium thiosulfate.
-
Administration of digoxin-specific immune antibody fragments can reverse life-threatening dysrhythmias from digoxin poisoning.
-
Use of 20% intravenous lipid emulsion can be efficacious in the resuscitation of life-threatening local anesthetic toxicity, especially from bupivacaine.
-
Patients with severe agitation from sympathomimetic poisoning require sedation to manage hyperthermia and acidosis, to prevent rhabdomyolysis and injury, and to allow evaluation for other life-threatening conditions.
-
Flumazenil reverses central nervous system and respiratory depression from benzodiazepine poisoning, but important risks and contraindications limit its use.
-
Venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation can be lifesaving for patients with cardiogenic shock or dysrhythmias that are refractory to other treatment measures. Because venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation implementation takes time, the process should be started early in patients who are not responding well to other therapies.
Références essentielles actualisées en 2023 (abonnés)
La suite est réservée aux membres et stagiaires du site.
Se connecter | Devenir membre | Devenir stagiaire
